A Systematic Review of IoT Integration on Health Monitoring System
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31033/ijemr.13.1.6Keywords:
Internet of Things, Patient Monitoring, Heart Rates, Blood Glucose, Parkinson's DiseaseAbstract
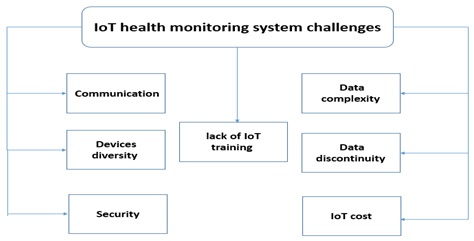
The Internet of Things (IoT) has had a significant impact on many fields, including the healthcare industry. It has, in particular, resulted in the development of devices that can collect and transmit data, allowing for better patient monitoring. IoT has enabled remote patient monitoring and telemedicine, which has significantly improved care. IoT wearable devices can collect and transmit data on patients' blood pressure, heart rates, and blood glucose levels. IoT could also help monitor hand hygiene compliance and track patients' moods and depression. Significantly, monitoring the symptoms of Parkinson's disease patients via IoT aids in disease management. These IoT applications have had significant implications in healthcare. IoT applications reduce healthcare costs while also improving treatment. The diagnosis becomes timely, allowing timely interventions to be implemented. IoT also enables proactive treatment and ensures the effective use and management of drug-related equipment. The main challenges are data security and the high initial implementation cost. In general, implementing IoT has had an impact on care delivery and resulted in better patient outcomes.
Keywords— Internet of Things, patient monitoring, heart rates, blood glucose, Parkinson's disease
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Haitham AlAdwani, Zahra

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.











