Variation of Temperatures with Rheological Properties of Water Based Drilling Fluid Containing Rice Husk and Other Additives
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31033/ijemr.13.1.13Keywords:
Rice Husk, Xanthan Gum, Bentonite, Chemical Additives, Rheological Properties, Drilling FluidsAbstract
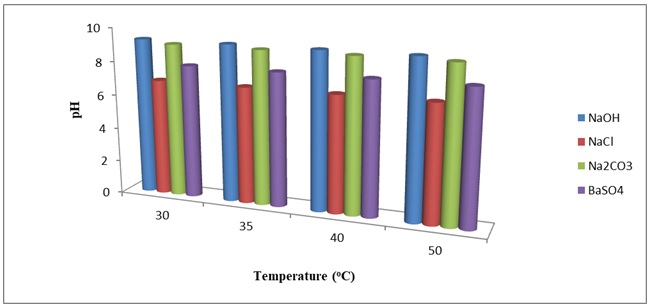
Drilling fluids rheological properties such as yield point (YP), plastic viscosity (PV), apparent viscosity (AV) and thixotropic property (Gel strength) are very important during drilling operations to prevent various drilling problems and improve the efficiency of the drilling process. Four water based drilling fluid samples containing different proportions of rice husk, xanthan gum and bentonite were investigated in this study to determine impacts of Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), Sodium chloride (NaCl), Sodium trioxocarbonate (IV) (Na2CO3) and Barite (BaSO4) on their rheological properties and pH values at temperature ranging from 30oC to 50oC. The chemical additives were added to the four samples at a given composition of 1%,2%,3% for (NaOH, NaCl, Na2CO3) and 5%, 10%, 15% for (BaSO4) by mass. The rheological properties of the samples were determined by FANN 35A viscometer using standard methods while pH meter and mud balance were used to measure their pH and density values respectively. The maximum pH, Shear- Stress, and AV corresponds to 11.6, 2.3985 Nm-2 and 112.5 cP respectively were observed in sample A with 10.5g of NaOH at 50oC while the highest YP value of 170 lbf/100ft2 was also observed at 35oC. However, maximum gel strength, GS (10 sec) and 10(min) were observed in the sample A with 190 lbf/100ft2 and 190 lbf/100ft2 for 10.5g of NaOH and 189 lbf/100ft2 and 191 lbf/100ft2 for 52.5g of BaSO4 respectively at temperature of 50oC. Furthermore, the same sample gave the lowest value of mud weight when the sample contain 3.5g of each additive (NaOH, NaCl and Na2CO3) at 35oC corresponds to 8.98 lb/gal. Drilling fluids produced with bentonite, rice husk, xanthan gum with appropriate proportion of NaOH and BaSO4 could be effective water based drilling fluid that can serve effectively in drilling operations at reasonable high temperature.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Akinyemi O. P., Abdulhadi A., Aliyu A.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.











