Feasibility of Water Hyacinth Ash as an Accelerator in Cement Slurry Formulation
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31033/ijemr.13.4.17Keywords:
Cement Slurry, Portland Cement, Water Hyacinth, Thickening Time, Accelerator AdditivesAbstract
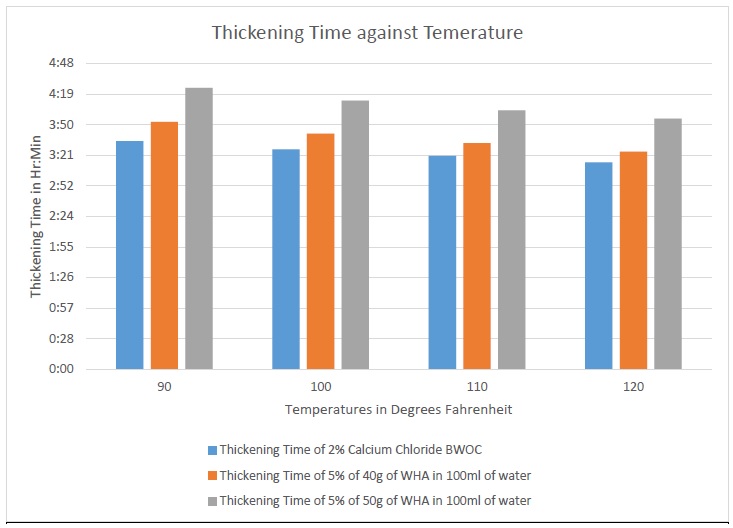
Cement is primarily used in drilling operations to protect the casing against the corrosive tendency of formation fluid and to support the casing with the external load on and around it. Cement slurry is formed by mixing water with Portland cement or with cement containing various essential additives as the case may be and pumping it down through to critical points in the annulus around the casing using various techniques. Class G cement is widely used in cementing jobs because it allows the use of accelerators and retarders for wide range of well depths and temperatures. Due to wait-on-cement time before commencement of drilling of the next section of the well, it is necessary to reduce the waiting time and it ripple effects on cost of drilling by introducing accelerator to the cement slurry. The chlorides of calcium, potassium and sodium are the commonly used accelerators. Water hyacinth ash have been known to contain high percentage of calcium, potassium and chlorine, these elements readily combine with water to form potassium chloride and calcium chloride of which both are used as accelerator additives in cement slurry formulation. The utilization of these compounds in water hyacinth ash as accelerator additives would be a major breakthrough in cementing jobs especially in shallow section of the wells. Locally sourced water hyacinth plants were dried and combusted in air, the ash was then activated with water and filtered. The filtrate was used to determine the thickening time of class G cement slurry and the results obtained was compared with that of inorganic calcium chloride. The thickening times at the various set temperatures for this experiment were close to the inorganic calcium chloride used. Though, the thickening time of cement slurry is dependent on temperature, the concentration of the accelerator in the slurry also affect it.. It was found out that water hyacinth ash reduces the thickening time of class G cement slurry comparatively and therefore, should be considered as accelerator additive in the formulation of oil well cement slurry for accelerating the cement setting time.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Neminebor Gift Pepe, Adewole Steve, Akpoturi Peters

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.











