Rainfall-Runoff Modelling using Artificial Neural Network: A Case Study of Banas River Catchment
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.31033/ijemr.13.2.43Keywords:
Rainfall-Runoff Modelling, Artificial Neural Network, Multiple Linear Regression, Water Balance Equation, Runoff Prediction, Banas River Catchment, GujaratAbstract
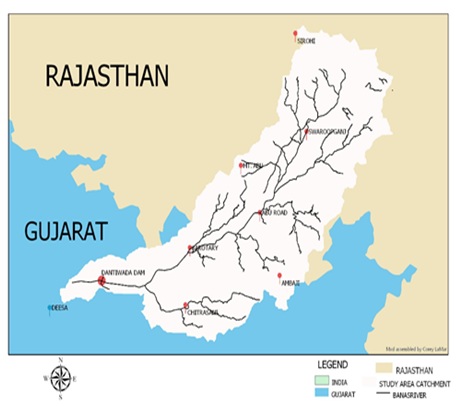
In the last two decades, Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) have become one of the most promising tools for modelling complex hydrological processes such as the Rainfall-Runoff interaction. The Artificial Neural Network could be used in cases where the availability of required data is limited. The Rainfall-Runoff model developed in this study was applied to the Banas River catchment of Gujarat, India. The hydrologic data were available for twelve years at CWC, Gandhinagar (such as Meteorological, weather, etc.). The Rainfall-Runoff model was developed by using an ANN technique (Feed-Forward Backpropagation algorithm) and a Multiple Linear Regression (MLR) method. The performance of both models was assessed by correlation coefficient (R), coefficient of determination (R2), and Mean Square Error (MSE). As the ANN gives only a black-box image, the sensitivity analysis was done to find the relative importance of input parameters. For the ANN models, the evaluation shows correlation coefficient (R) was obtained as 0.9318 whereas an MLR model, the correlation coefficient (R) was obtained as 0.8831. The RMSE values for the ANN and MLR models were 0.023535 and 0.15073 respectively. The results and analysis indicate that the ANN model provides better outcomes for datasets scaled between zero and one based on this study. In the comparison of both ANN and MLR models, the Artificial Neural Network technique was more suitable than the Multiple Linear Regression method. Hence the present study suggests that ANN models are an essential tool for predicting the hydrological responses in the Banas River Catchment.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Girish Parmar, Bhargav P Majmundar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.











